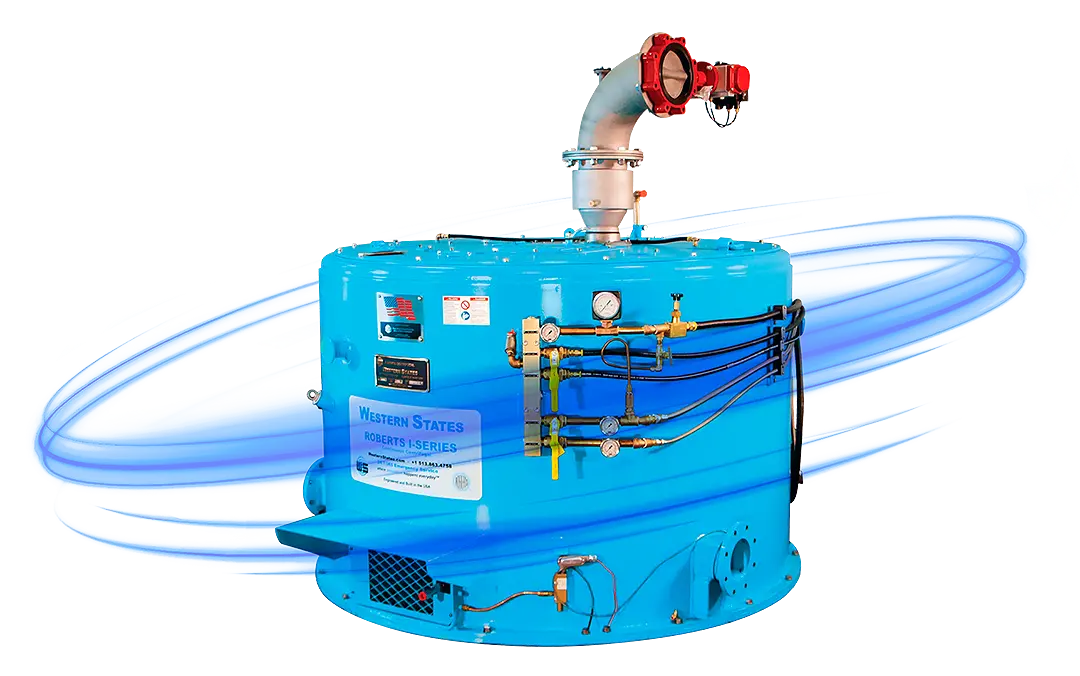
Introduction: The Maturation of an Industry
The global cannabis extraction market is undergoing a profound and rapid transformation. What began as a craft-based field is quickly maturing into a sophisticated, science-driven industry that mirrors the operational rigor of the pharmaceutical and food & beverage sectors.1 This evolution is fueled by a confluence of powerful forces: expanding global legalization, rising consumer demand for a diverse array of high-quality products like oils, concentrates, and edibles, and significant technological advancements in extraction methodologies.1 The market’s robust growth, projected to reach USD 8.41 billion in 2025, is a clear indicator of its immense potential.1
However, this growth is accompanied by increasing regulatory scrutiny. Governments worldwide are imposing strict compliance regulations, making technologies that ensure product safety, consistency, and traceability essential for legal operation and for building consumer trust.5 Consequently, the industry’s focus is shifting from the simple extraction of cannabinoids to the precise optimization of processes that yield high-purity, high-quality, and consistent final products.2
For extraction businesses to thrive in this new landscape, they must strategically invest in technology that addresses three converging megatrends: the dominance of cryogenic extraction for superior quality, the non-negotiable adoption of pharmaceutical-grade Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and the economic imperative of achieving true scalability and long-term profitability. This report will explore these defining trends in detail and demonstrate how purpose-built centrifuge technology stands as the cornerstone of a future-proof, competitive, and compliant extraction operation.
1. The Cold Standard: Why Cryogenic Ethanol Extraction is Defining the Future of Quality
While various extraction methods exist, cryogenic ethanol extraction has decisively emerged as the industry’s “cold standard.” Its unique ability to selectively extract desirable compounds—cannabinoids and volatile terpenes—while leaving undesirable materials like waxes, lipids, and chlorophyll frozen within the biomass results in a cleaner, higher-quality initial extract. This fundamentally streamlines the entire downstream process, enhancing both product quality and operational efficiency.8
The Science of Selectivity
The principle behind cryogenic ethanol extraction is elegantly simple and rooted in chemistry. At ultra-low temperatures, typically ranging from -40°C to -80°C, ethanol’s properties as a polar solvent become highly selective. It efficiently dissolves the target cannabinoids and terpenes, but its solvency for less desirable, non-polar compounds like plant waxes, fats, and chlorophyll is drastically reduced.11 These unwanted compounds remain frozen solid within the plant material, allowing for their easy separation.10
This selective process is paramount for preserving terpenes, the aromatic compounds responsible for the product’s flavor and fragrance, which are also believed to contribute to the therapeutic “entourage effect”.8 Terpenes are notoriously volatile and are the first compounds to degrade or evaporate when exposed to heat. Cryogenic extraction protects these delicate molecules. Scientific studies have demonstrated the critical importance of precise temperature control; for instance, terpene content can be over 50% lower when extracting at -20°C compared to a colder -40°C, a finding that highlights the necessity of deep, stable cooling capabilities.12
This method’s advantages become even clearer when compared to other common extraction technologies. Supercritical CO2 extraction, while clean, is generally less scalable, involves longer run times, and often co-extracts waxes that must be removed through a separate winterization step, adding time, labor, and cost to the workflow.9 Hydrocarbon extraction using solvents like butane or propane is efficient but poses significant safety risks due to high flammability and can leave residual solvents in the final product—a major concern for regulators and consumers.15 Finally, room-temperature ethanol extraction is far less selective, co-extracting large amounts of chlorophyll and waxes, which results in a harsh, bitter crude oil that requires extensive and costly post-processing to be viable.9
The Centrifuge as the Core Technology
The industrial centrifuge is the essential engine of the cryogenic ethanol extraction process. After the biomass has been soaked in chilled ethanol, the centrifuge performs the critical solid-liquid separation, spinning at high speeds to efficiently separate the cannabinoid-rich ethanol tincture from the spent plant material.16 To fully realize the benefits of this method, the centrifuge must be specifically engineered for precise temperature control. Features such as jacketed processing vessels and insulated components are not optional luxuries but core requirements for maintaining the ultra-low temperatures needed for selective extraction.18 The ability to consistently operate at temperatures as low as -40°C to -60°C is a critical performance indicator for any serious extraction facility.20
The strategic implications of adopting this technology are profound. The primary benefit of cryogenic extraction is not just a better product, but a fundamentally more efficient and profitable workflow. While methods like room-temperature ethanol or CO2 extraction pull unwanted waxes and lipids from the plant material, these impurities must then be removed in a separate, time-consuming, and resource-intensive post-processing step known as “winterization”.8 Cryogenic extraction, by preventing the initial co-extraction of these compounds, often eliminates the need for winterization altogether.21 Therefore, a higher upfront investment in a centrifuge with superior temperature control capabilities creates a significant downstream economic advantage. It removes an entire process step, which in turn reduces labor, solvent consumption, energy usage, and overall production time, leading to higher throughput and a healthier bottom line.
Furthermore, the consumer market is increasingly sophisticated, with products being differentiated based on their complete chemical profile. “Full-spectrum” and “broad-spectrum” extracts, which contain a wide array of cannabinoids and terpenes, command a premium price.4 Since cryogenic extraction is scientifically proven to be the most effective method for preserving these valuable and volatile terpenes, the choice of extraction technology directly dictates a company’s ability to compete in the high-margin, premium product segment.12 In this context, a centrifuge with precise temperature control is not merely a piece of equipment; it is a strategic tool for market positioning and brand differentiation.
The following table provides a clear comparison of the leading extraction technologies, highlighting the distinct advantages of the cryogenic ethanol method.
Table 1: Comparison of Modern Extraction Technologies
| Method | Solvent | Operating Principle | Key Advantages | Key Disadvantages | Ideal For |
| Cryogenic Ethanol | Ethanol | Low-temperature (-40°C to -80°C) solvent extraction to selectively dissolve cannabinoids/terpenes while leaving waxes frozen. 8 | High terpene preservation; high purity crude oil; often eliminates the need for winterization; highly scalable. 8 | Requires significant chilling capacity (energy intensive); requires high-purity ethanol. 9 | High-quality, full-spectrum extracts; large-scale production of distillates and isolates. |
| Room-Temp Ethanol | Ethanol | Solvent extraction at ambient temperatures. 10 | High extraction efficiency for cannabinoids; lower initial energy costs than cryogenic methods. 9 | Co-extracts high amounts of chlorophyll and waxes, requiring extensive post-processing (winterization, color remediation). 9 | Bulk crude oil production where extensive refinement is already part of the workflow. |
| Supercritical CO2 | Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | CO2 is pressurized and heated to a supercritical state, where it acts as a solvent to extract compounds. 13 | Clean, non-toxic, tunable selectivity; solvent is easily removed from final product. 13 | High capital cost for equipment; slower batch times; often requires a winterization step to remove co-extracted waxes. 9 | High-purity extracts for vape cartridges and specialty products; facilities prioritizing non-flammable solvents. |
| Hydrocarbon | Butane, Propane | Non-polar solvents wash over biomass to dissolve cannabinoids and terpenes. 13 | High efficiency; excellent terpene preservation; produces popular concentrates like shatter and wax. 15 | Highly flammable solvents require C1D1 environments and pose significant safety risks; potential for residual solvents in the final product. 13 | “Live resin” and other high-terpene concentrates for connoisseur markets. |

2. The GMP Imperative: Adopting Pharmaceutical Standards for Cannabis Processing
As the cannabis industry continues its march toward mainstream acceptance and federal oversight, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are rapidly transitioning from a voluntary best practice to a mandatory requirement. This fundamental shift, driven by regulatory bodies and consumer demand for safety, necessitates a complete overhaul of how extraction facilities are designed, equipped, and operated. Adherence to pharmaceutical-grade standards—prioritizing hygiene, safety, process validation, and contamination prevention—is becoming the new baseline for market entry and long-term success.5
Pillar 1: Sanitary by Design – The Foundation of GMP
The core principle of GMP is that quality must be built into the process, and this begins with the equipment itself. All processing equipment must be “sanitary by design,” meaning it is engineered to be easily and thoroughly cleaned, eliminating any potential for product accumulation or microbial growth.26
- Material Selection: GMP regulations mandate that all product-contact surfaces be non-reactive, non-toxic, and corrosion-resistant. For this reason, 316L stainless steel is the universally accepted standard in the pharmaceutical industry, offering superior resistance to chemical corrosion compared to other grades like 304 stainless steel.5
- Surface Finish: Surfaces must be smooth, non-porous, and free of pits, crevices, or “dead zones” where product or microbes can accumulate. A polished surface finish with a roughness average (Ra) of less than 0.8 micrometers is a common industry benchmark to ensure cleanability.26
- Hygienic Construction: This principle extends to the overall design, requiring features like self-draining surfaces to prevent fluid pooling, the use of sanitary fittings (e.g., Tri-Clamp) instead of threaded connections, and the elimination of dead legs in piping where cleaning solutions cannot reach.27
Pillar 2: Preventing Cross-Contamination with Clean-in-Place (CIP) Systems
Clean-in-Place (CIP) is an automated method for cleaning the interior surfaces of a processing line without disassembly. It is a critical component of a GMP-compliant facility, ensuring a consistent, repeatable, and validated level of cleanliness between batches.33 A typical CIP cycle involves a programmed sequence of steps, including an initial water rinse, a caustic wash to remove organic soils, an acid wash to remove mineral deposits, and final rinses to flush the system.33 For a centrifuge to be truly GMP-compliant, it must be designed for seamless CIP integration, featuring strategically placed spray balls for 100% surface coverage, smooth internal geometries, and the elimination of any dead zones where residue could hide.36
Pillar 3: The Validation Framework – Proving the Process Works
A cornerstone of GMP is validation—the process of creating documented evidence that a piece of equipment is installed correctly, operates as intended, and consistently produces the desired result. This is typically accomplished through a three-phase qualification process.38
- Installation Qualification (IQ): This is the documented verification that the equipment has been installed and configured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. It answers the question: “Is it installed correctly?”.38
- Operational Qualification (OQ): This phase involves testing the equipment to confirm that its systems and subsystems operate as intended throughout all specified operating ranges, including worst-case scenarios. It answers: “Does it work correctly?” and involves testing alarms, controls, and safety interlocks.38
- Performance Qualification (PQ): This is the final step, providing documented verification that the equipment, as installed and operated, can perform effectively and reproducibly under real-world conditions. It answers: “Does it consistently produce a quality product?” This requires running multiple consecutive batches with the actual product to demonstrate process stability and repeatability.38
Viewing GMP solely as a costly regulatory burden is a strategic misstep. In reality, GMP compliance is rapidly becoming a critical market access tool. As the global cannabis market matures, major jurisdictions like the European Union and Australia already mandate EU-GMP or equivalent certifications for medicinal cannabis products.42 As cannabis-derived products move closer to mainstream pharmaceutical and dietary supplement categories, GMP will become the universal standard.5 Large-scale distributors and pharmaceutical partners, to mitigate their own risk, will simply refuse to work with non-compliant producers.5 Therefore, investing in GMP-compliant equipment from the outset is a strategic investment in future revenue streams and global market access. A facility built to GMP standards can pivot to serve these high-value markets with ease, creating a significant competitive advantage over those who must undergo costly and time-consuming retrofits.
Furthermore, the initial choice of equipment has a profound, cascading effect on the entire operational viability of a GMP facility. A centrifuge with a poor sanitary design—for example, one constructed with 304 stainless steel, containing crevices, or lacking proper CIP integration—makes the cleaning validation process extraordinarily difficult, if not impossible. If it cannot be proven through documented evidence that the machine can be cleaned to a consistent, microbial-free level, it cannot be GMP-qualified.31 If the equipment is not qualified, the entire production process cannot be validated. This means the initial cost savings from purchasing non-compliant equipment are dwarfed by the immense long-term costs of validation failures, production delays, potential product recalls, and being permanently locked out of the industry’s most profitable markets. The design of the equipment, therefore, directly dictates business risk.
Table 2: Key Considerations for GMP-Compliant Centrifuge Selection
| GMP Principle | Key Feature/Specification | Why It Matters (The “So What?”) | Questions to Ask Your Supplier |
| Material Compatibility & Purity | All product-contact surfaces made of 316L Stainless Steel or other specified corrosion-resistant alloys. 5 | Prevents chemical leaching, corrosion, and contamination of the product. 316L is the pharmaceutical standard for purity and cleanability. | What materials are used for all wetted parts? Can you provide material traceability certificates? |
| Cleanability & Contamination Prevention | Smooth, polished surfaces (e.g., Ra<0.8μm); absence of crevices, threads, and dead legs; self-draining design. 26 | Eliminates areas where product or microbes can accumulate, ensuring the equipment can be thoroughly cleaned and sanitized to prevent cross-contamination between batches. | What is the surface finish on product-contact parts? How is the equipment designed to eliminate dead zones and ensure complete drainage? |
| Repeatable Cleaning | Integrated Clean-in-Place (CIP) system with strategically placed spray balls for 100% coverage. 32 | Automates the cleaning process for consistent, verifiable results. Eliminates human error and reduces downtime associated with manual cleaning. | Is the centrifuge designed for CIP? Can you provide spray ball coverage diagrams (e.g., riboflavin test results) to validate cleaning effectiveness? |
| Process Validation | Comprehensive documentation package including material certs, weld logs, drawings, and a detailed IQ/OQ protocol. 5 | Provides the necessary documented evidence for regulatory bodies (like the FDA) to prove the equipment is installed and operates correctly, which is a mandatory part of GMP. | Do you provide a full IQ/OQ/PQ documentation and validation support package? What is your experience with equipment qualification in regulated industries? |
| Operator & Environmental Safety | Explosion-proof motors and controls for hazardous locations (e.g., Class 1, Division 2). Sealed, pressure-tight design. 43 | Ensures safe operation when using flammable solvents like ethanol, protecting personnel and the facility. Prevents vapor emissions into the workspace. | What hazardous location ratings (e.g., C1D2) does the equipment carry? Are the motor and control panel certified by a recognized body (e.g., UL)? |
3. Precision and Repeatability: The Rise of Automation and Data-Driven Extraction
To meet the stringent demands of GMP and achieve the operational efficiencies required for profitability, the cannabis extraction industry is decisively shifting away from inconsistent manual processes toward fully automated systems. This technological leap is centered around the integration of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs). These systems are becoming standard, enabling precise, repeatable control over every critical process parameter and ensuring the production of a consistent, high-quality product, batch after batch.45
The Role of Automation in Modern Extraction
PLCs and HMIs serve as the “brain” and “face” of the modern industrial centrifuge. The PLC, a ruggedized industrial computer, executes pre-programmed recipes with absolute precision, controlling variables such as agitation speed, cycle times, ramp rates, and temperature. The HMI provides a user-friendly touchscreen interface that allows operators to select these recipes, monitor the process in real-time, and view critical data and alarms.45
The primary benefit of this automation is the elimination of process variability and human error. By executing a saved recipe identically every time, facilities can guarantee that their final product has a consistent cannabinoid and terpene profile. This level of consistency is non-negotiable for medical applications and is a cornerstone of building a trusted consumer brand.46 Furthermore, these automated systems empower process optimization. Operators can easily create, test, and save new recipes for different cannabis strains or to target specific end-products, facilitating rapid R&D and allowing for the fine-tuning of extraction parameters to maximize both yield and quality.46
Data Logging for Compliance and Improvement
A critical function of automated systems is their ability to log data. GMP regulations require extensive documentation and record-keeping to ensure full traceability for every product batch.5 An automated centrifuge can continuously log all critical process parameters—time, temperature, speed, valve positions—for every run, creating an unalterable digital batch record. This data stream dramatically simplifies regulatory audits and proves that a process was run within its validated parameters.45
This logged data is also an invaluable tool for Quality Assurance and continuous improvement. If a particular batch fails analytical testing, process engineers can immediately review the historical data to identify any deviations or anomalies that may have occurred during the extraction step. This enables highly effective troubleshooting and the implementation of Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA), a key component of any robust quality management system.46
Safety and Efficiency in Hazardous Environments
Safety is another paramount driver for automation. The use of flammable solvents like ethanol requires that extraction equipment be operated in classified hazardous locations, such as a Class 1, Division 2 (C1D2) environment. Automated systems that feature explosion-proof (XP) motors and C1D2-rated control panels are essential for ensuring operator safety and meeting stringent fire code regulations.19 Automation also enhances operational efficiency by reducing the need for constant operator oversight, freeing up skilled technicians to focus on higher-value tasks and directly lowering labor costs.6
A manual process that works perfectly at the bench scale often fails when scaled to production levels, primarily due to inconsistency. Process scale-up is a non-linear challenge; simply using a larger vessel does not guarantee a proportionally larger output of the same quality.51 Manual control introduces variability—one operator’s technique will always be slightly different from another’s—and this variability is magnified at a larger scale, leading to inconsistent batches and unpredictable yields.46 Automation is the fundamental mechanism that solves this problem by locking in the process. A recipe programmed into a PLC is executed identically every single time, regardless of the operator on shift. This transforms extraction from a variable “art” into a controlled, repeatable, and industrial “science,” which is an absolute prerequisite for any successful, large-scale, GMP-compliant operation.
Beyond compliance, the process data logged by these automated systems is rapidly becoming a strategic asset in its own right. The cannabis industry is still in the early stages of developing a deep, scientific understanding of how specific process parameters influence the final chemical profile of an extract.2 Facilities with robust data logging capabilities are effectively building a valuable internal database that correlates process inputs (time, temperature, agitation speed) with analytical outputs from the lab (cannabinoid potency, terpene profile). This data can eventually be analyzed using advanced tools like AI and machine learning to predict outcomes, create novel recipes optimized for specific chemical profiles (such as high-CBG or specific terpene ratios), and troubleshoot production issues with unprecedented speed and accuracy.3 In this light, the equipment is not just producing oil; it is generating the proprietary knowledge required to produce better oil more efficiently, creating a powerful competitive moat that is difficult for others to replicate.
4. Beyond the Sticker Price: A Strategic Approach to Scalability and Profitability
In a capital-intensive industry like cannabis extraction, one of the most critical financial mistakes a business can make is focusing solely on the upfront purchase price of equipment. A truly strategic approach to capital expenditure requires evaluating investments through the dual lenses of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and Return on Investment (ROI). This comprehensive financial analysis consistently reveals that premium, reliable equipment with a higher initial cost often delivers far greater long-term value by minimizing the immense, and often hidden, costs of downtime, maintenance, and lost productivity.53
The Fallacy of Upfront Cost
The initial purchase price of industrial machinery frequently represents only a small fraction—as little as 20-30%—of its total cost over a typical 10-year operational lifespan.56 Cheaper, less robust equipment often incurs significantly higher long-term costs due to more frequent repairs, higher energy consumption, lower efficiency, and reduced reliability, ultimately resulting in a much higher TCO and a lower return on investment.53
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
TCO is a financial framework designed to calculate the complete, holistic cost of an asset over its entire lifecycle, from acquisition and installation to operation, maintenance, and eventual disposal.58 For a production-scale extraction centrifuge, the TCO can be broken down as follows:
TCO=Ca+Co+Cm+Cp−Cd
Where:
- Ca = Initial Acquisition Cost: Purchase price, shipping, installation, commissioning, and initial operator training.61
- Co = Operating Costs: The ongoing costs of running the machine, including energy consumption, consumables like filter bags, and direct labor.63
- Cm = Maintenance Costs: The costs of scheduled preventive maintenance, spare parts inventory, and labor for repairs.63
- Cp = Downtime Costs: This is the most significant and frequently overlooked cost. It represents the lost revenue when the equipment is not operational and is calculated as:
LostRevenue=(Hours of Downtime)×(Avg. Production Rate/Hour)×(Gross Profit/Unit).64 - Cd = Residual Value: The resale value of the equipment at the end of its useful life, which is subtracted from the total cost.67
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
While TCO quantifies the total cost, ROI measures the profitability of that investment. It answers the fundamental business question: “How much profit will this equipment generate for every dollar invested?”.68 The formula is:
ROI(%)=Total Cost of InvestmentNet Profit from Equipment×100.62
Net profit is determined by the additional revenue generated (from higher throughput or new product capabilities) and cost savings (from reduced labor, solvent, or energy use), minus the ongoing operational and maintenance costs.62
The Challenge of Scaling
A major hurdle for growing extraction businesses is the transition from pilot-scale R&D to full-scale production. Industrial processes rarely scale linearly; equipment that performs well in a lab may fail under the rigorous demands of continuous, 24/7 operation.51 Successfully scaling requires investing in robust, industrial-grade equipment designed for high throughput and unwavering reliability. At this stage, durability and dependability become primary economic drivers.14
In a scaled extraction facility, unplanned downtime is the true “profit killer.” The financial impact of even a single hour of a key piece of equipment being offline can be catastrophic. A production-scale centrifuge can process hundreds of pounds of biomass per shift, generating crude oil valued in the tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars.71 When that centrifuge goes down, the entire downstream production line—from distillation to isolation—is starved of material, bringing the entire revenue-generating operation to a halt. The costs compound quickly, encompassing not just the lost production value but also idle labor, potential spoilage of in-process material, and the risk of missing critical delivery deadlines to customers.66 Industry-wide data indicates that a single hour of downtime can cost an organization over $100,000.56 This reality fundamentally reframes the purchasing decision. The most important question is not “How much does it cost to buy?” but rather, “How much will it cost me when it inevitably fails?” In this context, equipment reliability is not a mere feature—it is the single most important economic variable. A centrifuge that costs 20% more upfront but experiences 5% less unplanned downtime per year will deliver an exponentially better ROI over its lifespan.
This non-linear nature of scaling also introduces significant financial risk. Companies must often commit to millions of dollars in capital equipment based on R&D results from small, non-representative benchtop machines.51 There is a substantial risk that the chosen process or equipment will not perform as expected at full scale, leading to a failed investment and crippling financial losses. An equipment rental program provides a powerful strategic tool to mitigate this risk. By allowing a company to conduct pilot-scale trials using the
actual industrial-grade machine they intend to purchase, it de-risks the entire scale-up process.73 Processors can validate their process parameters, confirm yields and throughput, and train their operators
before committing to the full capital expenditure. A rental fleet is therefore not just a temporary fix for a broken machine; it is an essential tool for process development and data-driven capital decisions, bridging the perilous gap between R&D and full-scale production.
Table 3: The TCO Advantage: A Sample 5-Year Calculation Framework
| Cost Category | “Standard” Centrifuge (Lower Upfront Cost) | Western States Centrifuge (Higher Upfront Cost) | Notes / Assumptions |
| Acquisition Costs | |||
| Purchase Price | $200,000 | $250,000 | Premium for industrial-grade, durable construction. |
| Installation & Commissioning | $20,000 | $20,000 | Assumed to be similar for both. |
| Subtotal (Initial Investment) | $220,000 | $270,000 | |
| Annual Operating & Maintenance Costs | |||
| Energy Consumption | $15,000 | $12,000 | Higher efficiency motor and drive system. |
| Scheduled Maintenance & Spares | $10,000 | $5,000 | Fewer moving parts, higher quality components reduce maintenance needs. 76 |
| Annual Downtime Costs | Based on 250 operating days/year, 16 hrs/day. Lost revenue calculated at $10,000/hr. 56 | ||
| Unplanned Downtime (Hours/Year) | 80 hours (2% of operating time) | 20 hours (0.5% of operating time) | Higher reliability due to robust, proven design. 76 |
| Cost of Lost Production | $800,000 | $200,000 | The single largest differentiator in long-term cost. |
| Subtotal (Annual Costs) | $825,000 | $217,000 | |
| 5-Year Total Cost of Ownership | $4,345,000 | $1,355,000 | (Initial Investment + 5 x Annual Costs) |
| TCO Difference over 5 Years | $2,990,000 Lower TCO | The initial $50,000 premium yields nearly $3M in savings over five years. |

5. The Western States Advantage: Engineered for the Next Generation of Botanical Extraction
Western States is uniquely positioned to meet the rigorous demands of the modern cannabinoid extraction industry. This is not by adapting existing machinery, but by leveraging over a century of direct experience in building robust, reliable, and compliant centrifuges for the world’s most demanding industries, including sugar processing, fine chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. The Botanical Centrifuge (WSB) series is a purpose-built solution that directly addresses the converging trends of cryogenic quality, GMP compliance, and long-term profitability.78
Connecting Features to Industry Trends
- Cryogenic Excellence: The WSB series is engineered for optimal performance at the ultra-low temperatures required for modern extraction. The equipment’s design emphasizes precise temperature control, a non-negotiable factor for preserving the full spectrum of valuable cannabinoids and delicate terpenes during the cryogenic ethanol process.18 This capability directly aligns with the industry’s adoption of the “Cold Standard.”
- GMP-Ready by Design: Western States’ deep heritage in the Chem/Pharma sectors informs every aspect of their botanical equipment design.80 This legacy provides a powerful advantage in an industry now striving for pharmaceutical-grade standards.
- Materials and Construction: The company’s expertise with a wide range of materials, including 316L stainless steel and exotic alloys like Hastelloy, is a standard feature of their Chem/Pharma lines (such as the Quadramatic™) and is applied to the botanical series. This ensures material compatibility and the corrosion resistance essential for GMP compliance.82
- Sanitary Features: The designs prioritize ease of cleaning and sterilization. Features such as full-opening covers for complete internal inspection and options for integrated Clean-in-Place (CIP) systems are born from decades of meeting GMP principles in other industries.36
- Validation Support: Having long served regulated industries, Western States understands the critical importance of documentation. The company is equipped to provide the comprehensive support and documentation packages necessary for customers to successfully navigate the rigorous IQ, OQ, and PQ validation process.80
- Automated for Precision and Compliance: WSB centrifuges are equipped with state-of-the-art PLC controls and intuitive HMI touchscreens. This allows for the programming of precise, repeatable extraction cycles, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency and generating the detailed data logs required for GMP traceability and audits.82
- The TCO Proposition – “Legendary Dependability”: The core brand promise of “Legendary Dependability” is the very foundation of a low TCO. The fact that Western States centrifuges from the 1950s are still in service globally is a powerful testament to their robust engineering and exceptional long-term value.78 Features like heavy-duty bearings, superior suspension systems, and a “NEVER OBSOLETE” policy for parts and service directly translate to reduced maintenance costs and, most critically, minimized unplanned downtime—the largest driver of high TCO.84
- De-Risking Scalability with the Rental Program: Western States explicitly offers a rental fleet of equipment, including pilot-scale models, for on-site customer testing and process development.78 This program is a powerful strategic tool that allows processors to validate their cryogenic extraction process on an industrial-grade machine
before making a major capital investment, directly addressing one of the industry’s most significant financial and operational risks.79
The cannabis industry is currently evolving to meet the standards that the chemical and pharmaceutical industries have adhered to for decades. In this context, Western States’ century-long heritage is its most powerful differentiator. While many competitors are new companies learning the complexities of industrial manufacturing and regulatory compliance, Western States has been engineering solutions for environments where GMP, sanitary design, hazardous material handling (Class 1, Div 1/2), and 24/7 reliability are not new trends, but baseline requirements.80 The advanced features available on their Chem/Pharma centrifuges—such as pressure-tight construction, a vast array of exotic alloy options, and robust CIP systems—demonstrate a depth of engineering expertise that is directly transferable and immensely valuable to sophisticated cannabis processors.82 This positions Western States not as just another equipment vendor, but as an experienced technology partner capable of guiding customers through the industry’s complex maturation.
Furthermore, the rapid pace of innovation in cannabis technology can create investment hesitancy, as buyers fear their expensive new equipment may become obsolete.2 Western States’ “NEVER OBSOLETE” policy, coupled with a long history of providing modernization upgrades for machines that are decades old, directly counters this fear.84 This communicates a clear message: an investment in a Western States centrifuge is an investment in a long-term manufacturing platform, not a disposable piece of technology. It is a machine built to last for decades, with a proven pathway for future upgrades, transforming the purchase from a short-term tactical decision into a long-term strategic investment in a reliable and future-proof manufacturing foundation.
Table 4: Western States Botanical Centrifuge Models at a Glance
| Model | Max Biomass Capacity (lbs/cycle) | Typical Cycle Time (minutes) | Key Features & Benefits | |||
| WSB-15 | 15 lbs | 10–20 | Ideal for pilot-scale operations, R&D, and specialty batch production. Allows for process validation before scaling up. 18 | |||
| WSB-40 | 40 lbs | 10–20 | Production-scale capacity designed for high throughput. Engineered for user-friendly, single-operator use to simplify loading and unloading. 18 | |||
| All Models | N/A | N/A | Temperature Control: Designed for precise low-temperature regulation to preserve terpenes. 18 | GMP-Ready Options: Available with 316L stainless steel, CIP integration, and full documentation support. 80 | Safety & Compliance: Engineered with user safety as a priority; meets stringent industry standards. 18 | Durability: Basket optimized for long-term durability and balance, reflecting “Legendary Dependability.” 18 |
Conclusion: Partnering for Success in a Demanding Market
The future of successful and profitable cannabinoid extraction lies at the intersection of three powerful, converging trends: the pursuit of superior product quality, driven by cryogenic extraction methods; the necessity of unwavering regulatory compliance through the adoption of Good Manufacturing Practices; and the implementation of a smart economic strategy focused on scalability and long-term value through Total Cost of Ownership analysis. Navigating this complex and demanding landscape requires more than just machinery; it requires a technology partner with a deep understanding of industrial processes and a proven track record of reliability.
Western States stands apart not merely as a manufacturer, but as an essential partner for growth. The company’s legacy of “Legendary Dependability,” forged over a century of service to highly regulated industries, is embedded in every centrifuge they build. This deep expertise in sanitary design, hazardous environment safety, and 24/7 operational robustness provides the technological foundation that modern processors need. Combined with forward-thinking solutions like a strategic rental program to de-risk scalability and a “NEVER OBSOLETE” commitment to long-term value, Western States offers both the technology and the strategic support necessary to build a compliant, scalable, and profitable operation for the future.
The future of extraction demands more than just equipment; it demands a reliable partner with a proven track record. Contact our extraction specialists today to discuss how Western States can help you build a compliant, scalable, and profitable operation for the future.
Obras citadas
- Exploring Barriers in Cannabis Extraction Equipment Market: Trends and Analysis 2025-2033, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.datainsightsmarket.com/reports/cannabis-extraction-equipment-1972610
- Cannabis Technology Strategic Business Analysis Report 2025 | IoT Integration in Grow Operations Enhancing Environmental Monitoring and Control – Global Market Forecast to 2030 – ResearchAndMarkets.com – Business Wire, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20250708551201/en/Cannabis-Technology-Strategic-Business-Analysis-Report-2025-IoT-Integration-in-Grow-Operations-Enhancing-Environmental-Monitoring-and-Control—Global-Market-Forecast-to-2030—ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Cannabis Technology Market Share & Opportunities 2025-2032 – Coherent Market Insights, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/industry-reports/cannabis-technology-market
- Cannabis Extraction Market Size & Share 2025-2030 – 360iResearch, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.360iresearch.com/library/intelligence/cannabis-extraction
- GMP Compliant Extraction Equipment – Prodigy Processing Solutions, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://prodigyusa.com/gmp-compliant-cannabis-extraction-equipment/
- 7 must-have technologies for modern cannabis cultivators – MJBizDaily, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://mjbizdaily.com/7-must-have-technologies-for-modern-cannabis-cultivators/
- Cannabis Extraction Technology Advancements: Latest Innovations in Equipment & Extraction Methods – Root Sciences, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.rootsciences.com/blog/latest-innovations-in-cannabis-extraction-methods-equipments/
- The Cold Standard: How Low-Temperature Ethanol Extraction Preserves Cannabinoids and Terpenes – Western States Machine Company, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/the-cold-standard-how-low-temperature-ethanol-extraction-preserves-cannabinoids-and-terpenes/
- How Ethanol Extraction Maximizes Yield and Minimizes Costs – USA Lab, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.usalab.com/blog/ethanol-extraction-maximizes-yield-minimizes-costs/
- Comprehensive comparison of industrial cannabinoid extraction techniques: Evaluation of the most relevant patents and studies at pilot scale – Frontiers, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/natural-products/articles/10.3389/fntpr.2022.1043147/full
- Comprehensive comparison of industrial cannabinoid extraction techniques: Evaluation of the most relevant patents and studies at – Frontiers, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/natural-products/articles/10.3389/fntpr.2022.1043147/pdf
- (PDF) Cold Ethanol Extraction of Cannabinoids and Terpenes from Cannabis Using Response Surface Methodology: Optimization and Comparative Study – ResearchGate, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366198476_Cold_Ethanol_Extraction_of_Cannabinoids_and_Terpenes_from_Cannabis_Using_Response_Surface_Methodology_Optimization_and_Comparative_Study
- THC Extraction at Scale: The Future of Marijuana Processing – Central Processors NY, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.centralprocessorsny.com/thc-extraction-at-scale/
- Extraction Technology – True Scalability™ Nextleaf Solutions (CSE:OILS), fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.nextleafsolutions.com/extraction-technology/
- Cannabis Extraction Technologies: Impact of Research and Value Addition in Latin America, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/28/7/2895
- CBD Extraction Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide to the Cannabis Extraction Process, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://entexs.com/blog/cbd-extraction-made-simple-a-step-by-step-guide-to-the-cannabis-extraction-process/
- Exploring and Selecting Essential Cannabis Testing Equipment – The Lab Depot, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.labdepotinc.com/articles/exploring-and-selecting-essential-cannabis-testing-equipment.html
- Botanicals – Western States Machine Company, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/botanical-centrifuges/
- Unused- C1D1 Labs C1D2 30 Gallon Cold Centrifuge Extractor – Aaron Equipment, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.aaronequipment.com/usedequipment/cannabis-equipment/extraction-and-processing-equipment/c1d2-51352002
- US10493377B1 – Biomass extraction and centrifugation systems and methods – Google Patents, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://patents.google.com/patent/US10493377B1/en
- Cryogenic Ethanol Extraction Method: 6 factors – Buffalo Extraction Systems, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.buffaloextracts.com/knowledge/cryogenic-ethanol-extraction-method/
- Pilot-Scale Preparation of Broad-Spectrum CBD: Extraction Optimization and Purification using Centrifugal Partition Chromatography – PubMed, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40524919/
- The Future of Cannabis Extraction | MACH Technologies, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://machtechnologies.com/2024/02/29/future-of-cannabis-extraction/
- Understanding New York Cannabis GMP Standards | Distru, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.distru.com/cannabis-blog/understanding-gmp-standards-for-new-york-cannabis-operators
- GMP Certification in the Cannabis Industry: The Complete Guide, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.rootsciences.com/blog/gmp-certification-in-the-cannabis-industry-complete-guide/
- Hygienic Design Guide for Rotary Sifters in Sanitary Applications – Prater Industries, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://blog.praterindustries.com/hygienic-design-guide-for-rotary-sifters-in-sanitary-applications
- Achieving Hygiene Excellence: Sanitary Design in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing – Anderson Dahlen Inc., fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://andersondahlen.com/sanitary-design-in-pharmaceutical-manufacturing/
- Cannabis Products – Sample Preparation – Retsch, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.retsch.com/applications/cannabis-products-sample-preparation-for-quality-control/
- Cannabis Extraction Equipment – Steel & O’Brien, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.steelobrien.com/markets-served/extraction/
- TruSteel automated extraction and processing equipment, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://trusteel.com/solvents_part1/
- Ten Principles of Hygienic and Sanitary Design | Diversey – Solenis, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.solenis.com/en/resources/blog/ten-principles-of-hygienic-and-sanitary-design/
- Hygienic design of Flottweg decanter centrifuges – Flottweg SE, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.flottweg.com/engineering/decanter-features/hygienic-design/
- Definitive Guide for CIP Cleaning System – Neologic Engineers, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.neologicengineers.com/blogs/definitive-guide-for-cip-cleaning-system
- Clean-In-Place (CIP) Systems – Teledyne Labs, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.teledynelabs.com/markets/clean-in-place
- Clean-in-Place (CIP) Systems: Everything You Need to Know – Central States Industrial, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.csidesigns.com/blog/articles/clean-in-place-cip-systems
- Pharma Peeler Centrifuge for efficient liquid solids separation, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://comipolaris.com/pharma-peeler-centrifuge/
- Horizontal peeler centrifuge HX/GMP – Pharma – Comi Condor, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.comicondor.com/en/horizontal-centrifuges/peeler-centrifuge-hxgmp
- What is IQ, OQ, PQ? [Quick Guide to Process Validation], fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.greenlight.guru/blog/iq-oq-pq-process-validation
- IQ, OQ, PQ: what’s needed for equipment validation in life sciences? – Cognidox, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.cognidox.com/blog/iq-oq-pq-equipment-validation
- A Guide to IQ, OQ, and PQ in FDA-Regulated Industries – Egnyte, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.egnyte.com/guides/life-sciences/iq-oq-and-pq
- A Basic Guide to IQ, OQ, PQ in FDA-Regulated Industries, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.thefdagroup.com/blog/a-basic-guide-to-iq-oq-pq-in-fda-regulated-industries
- GMP Facility for Cannabis Extraction and Finished Products – MECART Cleanrooms, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.mecart-cleanrooms.com/learning-center/building-a-gmp-facility-for-cannabis-extraction-and-finished-products/
- Hemp Extraction Centrifuge | Industrial Scale, Continuous Processing, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://dolphincentrifuge.com/hemp-extraction-centrifuge/
- Explosion Proof Stainless Steel Centrifuge | Alfa Laval Disc Stack Type, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://dolphincentrifuge.com/explosion-proof-stainless-steel-centrifuge/
- Extraction – Unitronics, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.unitronics-cannabis.com/industry/extraction-industry-solutions/
- Automation and All-In-One Systems – Cannabis Science and Technology, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.cannabissciencetech.com/view/automation-and-all-in-one-systems
- Siemens PLC Programming for Grow Room Automation | DMC, Inc., fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.dmcinfo.com/our-work/siemens-plc-programming-for-grow-room-automation/
- Automated Solvent Skid Control with a Schneider Electric Modicon PLC | DMC, Inc., fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.dmcinfo.com/our-work/automated-solvent-skid-control-with-a-schneider-electric-modicon-plc/
- cGMP Compliance Regulations – Advanced Extraction Labs, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://advancedextractionlabs.com/cgmp-regulations/
- Ethanol Extraction Centrifuge UL-Listed with C1D2 Rating 35lb / Run – Cedarstone Industry, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://cedarstoneindustry.com/product/ethanol-extraction-centrifuge-ul-listed-c1d2-rating-35lb-run/
- Challenges with Process Scale Up in Cannabis/Hemp Extraction, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://cannabisindustryjournal.com/feature_article/challenges-with-process-scale-up-in-cannabis-hemp-extraction/
- How Cannabis Tech is Evolving in 2025 – CloudBox, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.cloudboxapp.com/blog-posts/how-cannabis-tech-is-evolving-in-2025
- What Is Total Cost of Ownership in Manufacturing (And How Does it Impact Your Company’s Bottom Line?) – EAM-Mosca, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.eammosca.com/news/newsdetail/what-is-total-cost-of-ownership-in-manufacturing-and-how-does-it-impact-your-company-s-bottom-line-2858
- Total Cost of Ownership in Spend Analytics: Guide for Procurement Professionals – GEP, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.gep.com/blog/strategy/tco-in-spend-analytics-for-procurement-professionals
- Total Cost Of Ownership Delivers Best Analysis For Capital Packaging Equipment Purchasing – Food Online, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.foodonline.com/doc/total-cost-of-ownership-delivers-best-analysis-for-packaging-equipment-purchasing-0001
- How much does 1 hour of downtime cost the average business? – Rand Group, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.randgroup.com/insights/microsoft/how-much-does-1-hour-of-downtime-cost-the-average-business/
- How to Optimize Your Procurement Process to Reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://acteusgroup.com/procurement-process-to-reduce-total-cost-of-ownership-tco
- Total Cost of Ownership: How It’s Calculated With Example – Investopedia, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.investopedia.com/terms/t/totalcostofownership.asp
- Estimating Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) – Galorath, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://galorath.com/blog/total-cost-of-ownership/
- Building a Total Cost of Ownership model to support manufacturing asset lifecycle management | Request PDF – ResearchGate, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333692404_Building_a_Total_Cost_of_Ownership_model_to_support_manufacturing_asset_lifecycle_management
- How to Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) of CMMS – FieldCircle, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.fieldcircle.com/articles/how-to-calculate-total-cost-of-ownership/
- The Ultimate Guide To Equipment ROI Calculation – them.Net, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://them.net/the-ultimate-guide-to-equipment-roi-calculation/
- Disc Stack Centrifuge | Benefits, Costs, Operation, Specs, Sizing, Etc., fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://dolphincentrifuge.com/disc-stack-centrifuge/
- pluto-men.com, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://pluto-men.com/how-calculate-cost-of-downtime-in-manufacturing/#:~:text=Determine%20the%20number%20of%20units,the%20gross%20profit%20per%20unit.
- Free Downtime Calculator for Manufacturers – Boulter Industrial Contractors, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.boulterindustrial.com/resources/downtime-calculator
- How to Calculate the Cost of Downtime in Manufacturing? – Plutomen, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://pluto-men.com/how-calculate-cost-of-downtime-in-manufacturing/
- Procurement 101: Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) – How to Leverage and Improve it – CADDi, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://us.caddi.com/resources/insights/total-cost-ownership
- ROI: Return on Investment Meaning and Calculation Formulas – Investopedia, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/10/guide-to-calculating-roi.asp
- What Is Return on Investment (ROI) and How to Calculate It – Investopedia, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/returnoninvestment.asp
- The Future of Cannabis Processing: Scaling Without Losing Quality, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.cultivaphs.com/blog/the-future-of-cannabis-processing-scaling-without-losing-quality
- C1D1 Labs C1D2 Certified 30 Gallon Centrifuge System – Scientific Solutions, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.scisolinc.com/product/c1d1-labs-c1d2-certified-30-gallon-centrifuge-system/
- How to Calculate Downtime Costs – Understanding the Financial Impact – Peoplegeist, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.peoplegeist.com/en/how-to-calculate-downtime-costs-financial-impact-production
- Rental Centrifuges – Western States Machine Company, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/rental-centrifuges/
- Centrifuge Rental Services – Trucent, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.trucent.com/services/centrifuge-rental/
- Rent Alfa Laval Centrifuges | Fast Delivery & Expert Support – Diamond T Services, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://diamondtservices.com/centrifuge-rentals/
- Industrial Centrifuge Buying Guide: Key Factors to Consider – Sentrimax, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://sentrimax.com/news/industrial-centrifuge-buying-guide-key-factors-to-consider/
- Industrial Centrifuge | Types, Applications, Cost & Benefits, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://dolphincentrifuge.com/industrial-centrifuge/
- The Leading Centrifuge Manufacturer | Western States Machine Co, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/
- Informe Estratégico SEO – Western States.docx
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Centrifuges – Western States Machine Company, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/chem-pharma/
- Product Overview for the Sugar Industry – CMG Pumps, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, http://cmgpumps.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Western-States-Brochure.pdf
- The Quadramatic™ Centrifuge Machine – Western States, fecha de acceso: agosto 13, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/products/the-quadramatic-centrifuge-machines/
- Quadramatic Batch Centrifuges from Western States, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, http://www.separatorengineering.com/ws_chemical_centriuges_quadramatic.htm
- Common Challenges with Pharmaceutical & Chemical Separation, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/common-challenges-pharmaceutical-chemical-separation/
- Titan Batch Centrifuge – Western States, fecha de acceso: agosto 29, 2025, https://www.westernstates.com/products/titan-batch-centrifugal/